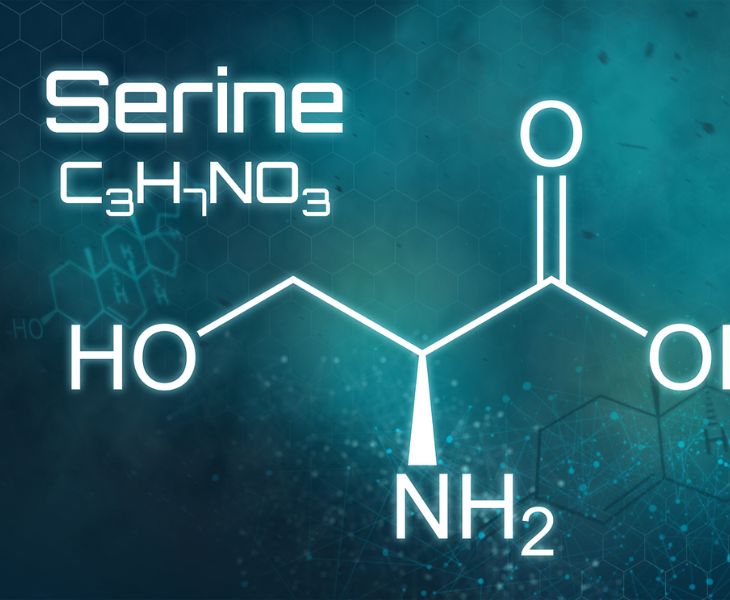
A Brief Introduction to L-Serine
Molecular Formula:C3H7NO3
Molecular Weight:: 105.09
CAS No.:56-45-1
Appearance:White crystals or crystalline powder
Regular commercial package: 25kg/drum
Benefits of L-Serine
- L-Serine improves memory and cognitive function, maintaining brain nerve cell communication.
- L-Serine relieves anxiety, relaxes the mind, and promotes sleep quality.
- L-Serine participates in protein synthesis and repairs damaged cells and skin.
- L-Serine promotes immunoglobulin production, boosting the body’s immunity.
If you have any questions about processing L-Serine, Highassay’s R&D team is here to help.


L-Serine VS D-Serine
L-Serine, in liquid form, is distributed throughout the body and participates in most bodily functions, providing energy. D-Serine, on the other hand, is primarily found in the brain. Acting as an NMDA receptor agonist, it can help regulate and improve neurological problems such as memory loss.
What is L-Serine?
L-Serine is a non-essential amino acid synthesized from glycine in the human body and can be obtained through food or supplements. L-Serine supports the immune system by promoting the metabolism of fat and fatty acids. It also participates in protein synthesis, plays a vital role in muscle growth and repair, and boosts immunity.
Benefits of Fat to the Human Body
- Energy Supply: It provides significantly more energy than carbohydrates and protein, making it the body’s primary energy source.
- Maintaining Body Temperature: It helps us withstand low temperatures, maintaining our internal body temperature and providing insulation.
- Protecting Organs: It reduces damage to organs, internal organs, and vital parts of the body caused by external impacts, providing protection.
- Promoting Vitamin Absorption: It aids the absorption and transport of fat-soluble vitamins, increasing their utilization by the body.
Benefits of Fatty Acids to the Human Body
In addition to the functions of fat, fatty acids also possess functions not found in fat, such as participating in cell composition and regulating metabolism. Because fatty acids are typically present in liquid form in the body, their fluidity determines their intercellular distribution.
Applications of L-Serine
Highassay adheres to strict quality control (QC) to produce L-Serine. Buy L-Serine in bulk from us now to get competitive market prices.
 Food Additives
Food AdditivesGenerally purchased and taken as nutritional supplements. Available in powdered form for dissolving in water or adding to various beverages for a more palatable texture, they can also be taken in capsule form for easier consumption.
 Cosmetics
CosmeticsAdded to cosmetics as a skin nourishing additive, L-Serine acts as a natural moisturizer. Besides whitening and moisturizing effects, it also has anti-wrinkle properties. Its high safety profile makes it well-suited for cosmetics.

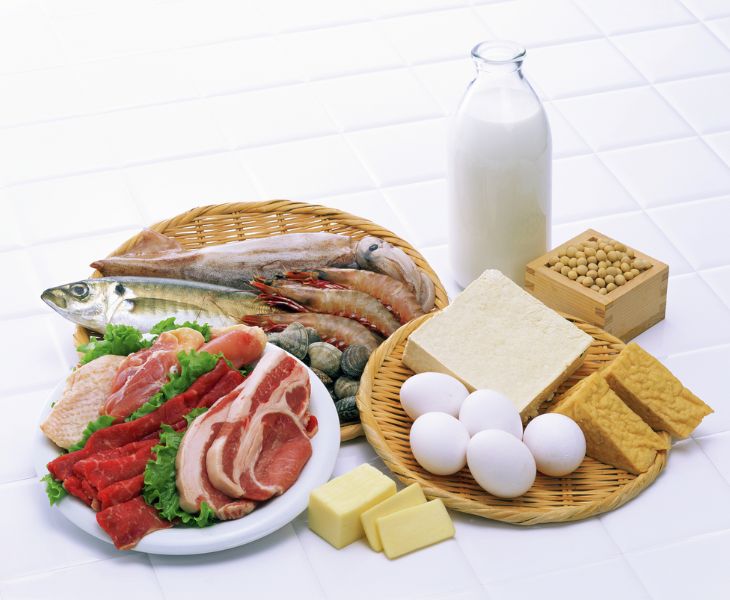
Foods Rich in L-Serine
- Animal foods: Meats such as chicken, beef, pork, and salmon
- Dairy products: Milk, cheese, yogurt, and other dairy products
- Eggs: Whole eggs such as chicken and duck eggs, especially those with a higher protein content
- Beans: Soybeans, lentils, chickpeas, and other legumes
- Nuts: Sesame seeds, almonds, and sunflower seeds
- Grains: Oats, brown rice, and others

About L-Serine
- First and foremost, it’s important to understand that L-Serine itself is not carcinogenic. However, high levels of L-Serine in the human body can accelerate the growth and reproduction of cancer cells. Therefore, L-Serine supplements are not recommended for cancer patients. This research finding also provides some direction for cancer treatment.
- L-Serine is not recommended for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease, and there is no definitive evidence that it is beneficial in alleviating symptoms.
- Demand for L-Serine is increasing with its wide range of uses, and the extraction and synthesis technologies for L-Serine are becoming increasingly sophisticated.
- Daily L-Serine intake should not exceed the safe range for the human body. Excessive intake can easily cause gastrointestinal discomfort and, in more severe cases, may lead to epilepsy.

Specification of L-Serine
| L-Serine | CP2020 | EP11 | USP2023 | AJI92 |
| Assay | ≥98.5% | 98.5-101.0% | 98.5-101.5% | 99.0-101.0% |
| PH | 5.5-6.5 | / | / | 5.2-6.2 |
| Specific rotation[a]D20 | +14.0°-+15.6° | +14.0°-+16.0° | / | +14.4°-+15.5° |
| Specific rotation[a]D25 | / | / | +14.0°-+15.6° | / |
| Transmittance(T430) | ≥98.0% | / | / | ≥98.0% |
| Appearance of solution | / | clear & colorless ≤BY6 | / | / |
| Chloride(Cl) | ≤0.02% | ≤0.02% | ≤0.05% | ≤0.02% |
| Ammonium(NH4) | ≤0.02% | ≤0.02% | / | ≤0.02% |
| Sulfate(SO4) | ≤0.02% | ≤0.03% | ≤0.03% | ≤0.02% |
| Iron(Fe) | ≤10PPM | ≤10PPM | ≤30PPM | ≤10PPM |
| Heavy metals(Pb) | ≤10PPM | / | / | ≤10PPM |
| Arsenic | ≤1PPM | / | / | ≤1PPM |
| Other amino acids | ≤0.50% | / | Individual impurities≤0.5% Total impurities≤2.0% | conform |
| Ninhydrin-positive substances | / | Individual impurities≤0.20% Total impurities≤0.5% | / | / |
| Loss on drying | ≤0.20% | ≤0.50% | ≤0.20% | ≤0.20% |
| Residue on ignition | ≤0.10% | ≤0.10% | ≤0.10% | ≤0.10% |
| Endotoxin | <12EU/g | <12EU/g | <12EU/g | / |
| Total plate count | ≤ 1000 CFU/g | ≤ 1000 CFU/g | ≤ 1000 CFU/g | ≤ 1000 CFU/g |
| Moulds & Yeasts | ≤ 100 CFU/g | ≤ 100 CFU/g | ≤ 100 CFU/g | ≤ 100 CFU/g |