A Brief Introduction to L-Methionine
Molecular Formula: C5H11NO2S
Molecular Weight: 149.211
CAS No.: 63-68-3
Appearance: White crystalline powder
Regular commercial package: 25kg/drum
Benefits of L-Methionine
- L-Methionine increases glutathione levels, which aids liver detoxification. Therefore, L-Methionine supplementation is particularly important for those who tend to stay up late or drink alcohol.
- As a precursor to glutathione, L-Methionine helps protect against free radical damage while promoting protein synthesis, benefiting overall health and slowing aging.
- L-Methionine promotes the synthesis of serotonin and dopamine, regulating the brain’s central nervous system, improving mood and relieving mild depression.
- L-Methionine participates in collagen synthesis, contributing to bone strength and joint health.
- L-Methionine promotes fat metabolism, breaking down body fat, and can be used in weight loss products.
If you have any questions about processing L-Methionine, Highassay’s R&D team is here to help.

What is L-Methionine?
L-Methionine is a sulfur-containing essential amino acid that cannot be synthesized naturally by the human body and must be obtained through food or supplements. L-Methionine plays a crucial role in the body, aiding protein synthesis, enhancing antioxidant capacity, enhancing cell repair and regulation, and detoxifying the body to protect liver function. In short, it is essential for overall human health.
Applications of L-Methionine
Highassay adheres to strict quality control (QC) to produce L-Methionine. Buy L-Methionine in bulk from us now to get competitive market prices.
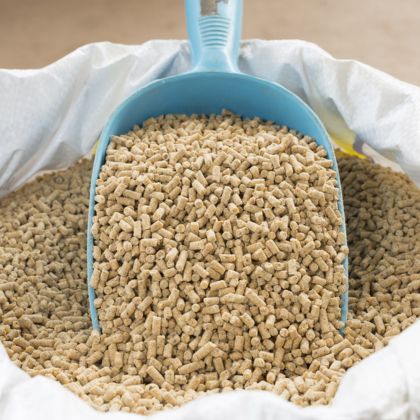 Animal Feed
Animal FeedEffectively promotes growth and boosts immunity. It is an essential amino acid that animals cannot synthesize on their own, so it must be supplemented through animal feed.
 Food Industry
Food IndustryAdded as a nutritional supplement to grains and legumes, and also to baby food, it helps infants and young children supplement L-Methionine, promote protein synthesis, and prevent malnutrition.
 Medical
MedicalUsed as an adjunct to the treatment of liver diseases (such as fatty liver disease and cirrhosis).Used as an antidote to help remove heavy metal toxins such as lead and mercury from the body
 Biological Research
Biological ResearchUsed as a protein cell culture medium and in other scientific research.
Sources of L-Methionine and L-Methionine Dosage
Supplementation is primarily through daily foods. Foods high in L-Methionine include meat, eggs, dairy products, soy, oats, sesame seeds, and Brazil nuts. Note that for vegetarians, plant-based foods contain lower levels of L-Methionine, so supplementation may be necessary. Besides vegetarians, even picky eaters may need a moderate supplement. While adequate L-Methionine intake is crucial for human health and has no side effects, daily supplementation should be within a safe range. Excessive intake can cause a range of adverse reactions, such as nausea and vomiting, and in severe cases, metabolic disorders. The dosage of supplements should be considered based on various factors, including individual health conditions, age, gender, and weight.


Storage of L-Methionine
- Sealed storage: This prevents exposure to oxygen and moisture, which can affect product quality.
- Dry storage: A humid environment can cause L-Methionine to decompose and reduce its activity.
- Store away from light: L-Methionine is light-sensitive. Direct sunlight can cause it to break down and become ineffective.
- Properly ventilate: Store in a well-ventilated warehouse to prevent the accumulation of harmful substances.
- Avoid direct contact: Avoid direct contact of L-Methionine with skin and eyes to prevent irritation.
L-Methionine VS SAMe
SAMe is a naturally occurring molecule synthesized from L-Methionine that acts as a methyl group donor in biochemical reactions in the body. SAMe is widely known as a nutritional supplement and antioxidant, promoting overall health.

Specification of L-Methionine
| L-Methionine | CP2020 | EP11 | USP2023 | USP40 | AJI92 |
| Assay | ≥98.5% | 99.0-101.0% | 98.5-101.5% | 98.5-101.5% | 99.0-100.5% |
| PH | 5.6-6.1 | 5.5-6.5 | 5.6-6.1 | 5.6-6.1 | 5.6-6.1 |
| Specific rotation[a]D20 | +21.0°-+25.0° | +22.5°-+24.0° | / | / | +23.0°-+24.5° |
| Specific rotation[a]D25 | / | / | +22.4°-+24.7° | +22.4°-+24.7° | / |
| Transmittance(T430) | ≥98.0% | / | / | / | ≥98.0% |
| Appearance of solution | / | clear & colorless | / | / | / |
| Chloride(Cl) | ≤0.02% | ≤0.02% | ≤0.05% | ≤0.03% | ≤0.02% |
| Ammonium(NH4) | ≤0.02% | ≤0.02% | / | ≤0.02% | |
| Sulfate(SO4) | ≤0.02% | ≤0.03% | ≤0.03% | ≤0.03% | ≤0.02% |
| Iron(Fe) | ≤15PPM | ≤10PPM | ≤30PPM | ≤30PPM | ≤10PPM |
| Heavy metals(Pb) | ≤10PPM | / | / | ≤15PPM | ≤10PPM |
| Arsenic | ≤1PPM | / | / | / | ≤1PPM |
| Other amino acids | ≤0.5% | Each impurity≤ 0.1% Total impurities≤ 0.3% | Methionine sulfoxide≤0.1% N-Acetyl-D,L-methionine≤0.2% Any unspecified impurity≤0.1% Total unspecified impurities≤0.3% | Individual impurities≤0.5% Total impurities≤2.0% | conforms |
| Ninhydrin-positive substances | / | / | / | / | / |
| Loss on drying | ≤0.2% | ≤0.50% | ≤0.3% | ≤0.3% | ≤0.20% |
| Residue on ignition | ≤0.1% | ≤0.10% | ≤0.4 | ≤0.4 | ≤0.10% |
| Endotoxin | <25 EU/g | <25 EU/g | <25 EU/g | / | / |
| Total plate count | ≤ 1000 CFU/g | ≤ 1000 CFU/g | ≤ 1000 CFU/g | ≤ 1000 CFU/g | ≤ 1000 CFU/g |
| Moulds & Yeasts | ≤ 100 CFU/g | ≤ 100 CFU/g | ≤ 100 CFU/g | ≤ 100 CFU/g | ≤ 100 CFU/g |





