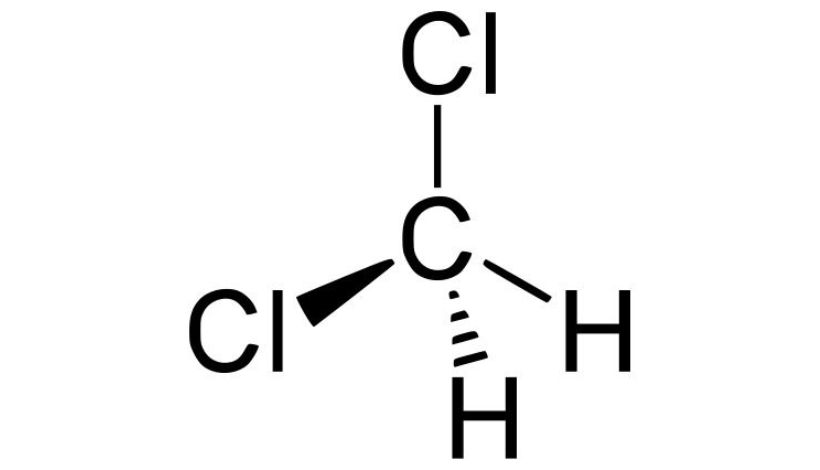
A Brief Introduction to Methylene Chloride
Molecular Formula: CH2Cl2
Molecular Weight: 84.93
CAS No.: 75-09-2
Appearance: Colorless transparent liquid
What is Methylene Chloride?
Methylene Chloride, also known as Dichloromethane, is a colorless organic solvent with a pungent odor. Methylene chloride is slightly soluble in water, soluble in ethanol and ether, and has the physical properties of being non-flammable, having a low boiling point, and being highly volatile. It is widely used in the pharmaceutical, plastics, and film industries.
According to incomplete statistics, Methylene Chloride accounts for 50% of total consumption in film production, 20% in the pharmaceutical industry, 20% in cleaning agents and the chemical industry, and 10% in other applications.
Highassay’s Methylene Chloride
As a Methylene Chloride supplier from China, Highassay offers various grades of Methylene Chloride raw materials that meet different industry standards. We have the most advanced production equipment and processes to ensure the high stability of the specifications of different batches of Methylene Chloride raw materials, and we provide MSDS with our products. We have a stable supply capacity to meet market demand. If you need to purchase Methylene Chloride raw materials, please choose Highassay!
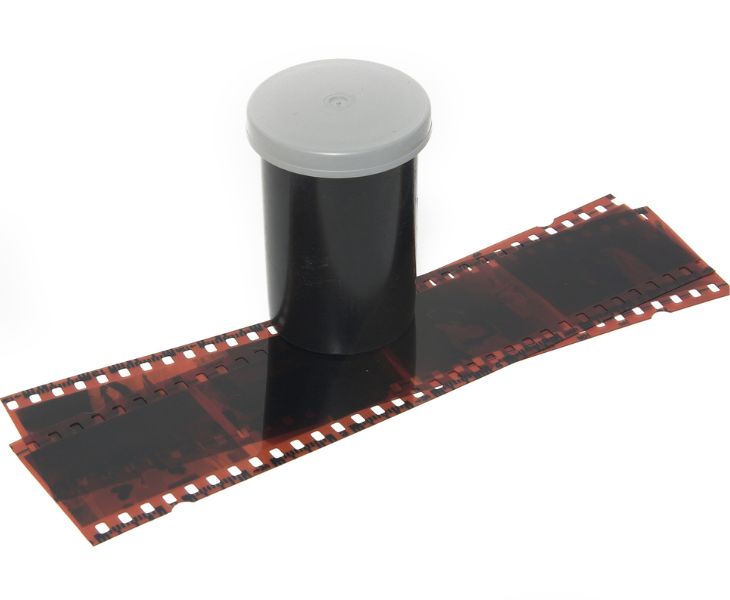
The important role of Methylene Chloride in film production
- Traditional photographic film bases are made from cellulose triacetate, and Methylene Chlorideis an important solvent in the production of high-quality cellulose triacetate film bases.
- The excellent dissolving properties of Methylene Chlorideallow cellulose triacetate particles to dissolve in the Methylene Chloride solvent, forming a viscous, homogeneous, and impurity-free solution.
- The low boiling point of Methylene Chlorideoffers the advantage of rapid evaporation, which shortens drying time and saves energy and equipment space in the production of cellulose triacetate film base.
- Methylene Chlorideis volatile, and by completely evaporating the residual Methylene Chloride from the cellulose triacetate film base, its optical purity and chemical stability are ensured.
- The non-flammability of Methylene Chlorideis also a key factor in ensuring safe production, as large amounts of solvent vapor are produced during the manufacturing process.


Applications of Methylene Chloride in the pharmaceutical field
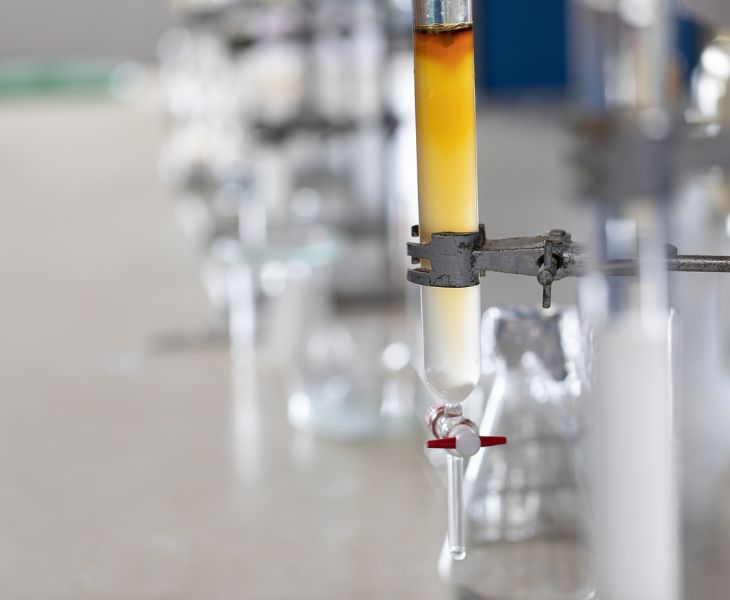
Reaction solvent:
- Serves as the reaction medium for active pharmaceutical ingredients and synthesis processes, providing favorable conditions for low-temperature reactions and inert environments.
- For examples: the synthesis routes of antibiotics and cardiovascular drugs.
Drug extraction solvent:
- Methylene Chloride’s strong solubility for organic compounds makes it useful for the separation and extraction of compounds from mixtures or fermentation broths.
- Methylene Chloride’s non-flammability is often considered as an alternative to flammable diethyl ether and petroleum ether.
- Methylene Chlorideis almost immiscible with water, thus reducing product loss.
- Methylene Chloride’s low boiling point facilitates its evaporation and removal from the product.
- For example, in large-scale production (large extraction tanks), its density greater than water facilitates the easy separation of the extract from water.
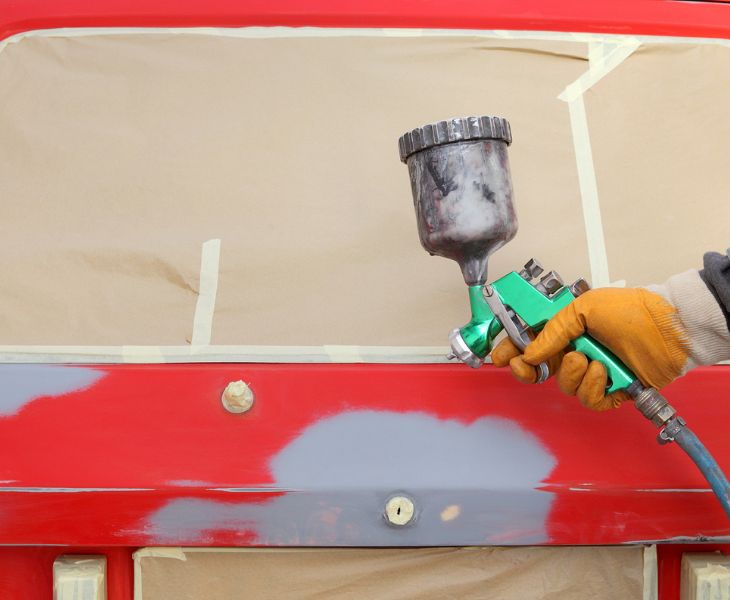
Applications of Methylene Chloride in cleaning agents and the chemical industry
Cleaning agent:
- Paint removers and coating strippers:Methylene Chloridecan quickly dissolve or swell paints, coatings, and other substances. It is not only highly efficient but also helps protect the underlying substrate from damage. It is commonly used for paint removal in aircraft, ships, automobiles, furniture restoration, and large equipment maintenance.
- Metal cleaning or degreasing: Methylene Chloridecan remove grease from the surface of parts, leaving them clean and residue-free, which is beneficial for subsequent operations such as painting and electroplating.
- Precision electronic cleaning agent: Methylene Chloridenot only has strong cleaning power and leaves no residue, but it also does not damage the electronic components themselves.
Chemical industry:
- Solvent:Methylene Chlorideis an important solvent in the production of agricultural products (pesticides, herbicides, etc.), fragrances, dyes, and other fine chemicals.
- Extraction and separation: Methylene Chloridecan be used in chemical production processes to extract specific components (from mixtures).
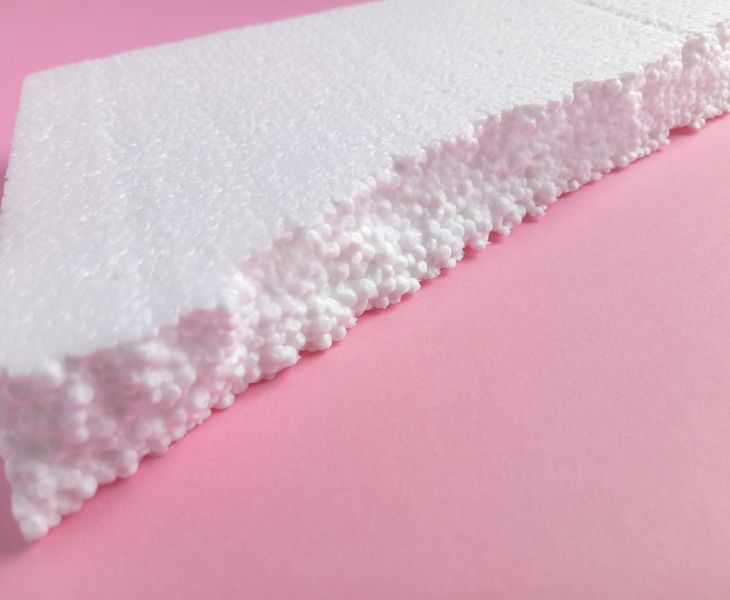


Other applications of Methylene Chloride (with examples)
Blowing agent:
Methylene Chloride is used as a physical blowing agent in the production of foamed plastics. Through vaporization, it produces lightweight foam with good thermal insulation properties and uniform cell structure, which is used in building insulation and packaging industries.
Adhesive:
Methylene Chloride is a powerful solvent for many plastics. It achieves seamless bonding by rapidly dissolving the plastic surface, offering ease of use and low cost.
Specification of Methylene Chloride
- Specification of Methylene Chloride
| Product Name | Methylene Chloride |
| Melting Point | -97℃ |
| Boiling Point | 39.8℃ |
| Water-Soluble | Slightly soluble in water |
| Density | 1.325g/cm³ |
| Lgnition Temperature | 556℃ |
| Flash Point | -14.1℃(No flash point at normal temperature and pressure) |
| Saturated Vapor Pressure | 46.5kPa(20℃) |
| Appearance | Colorless, transparent, and highly volatile liquid |
| Package | Sealed, corrosion-resistant container(Galvanized Steel Drum) |
| Storage | Cool, well-ventilated, and dry |
Methylene Chloride is used as a solvent to remove caffeine from coffee beans or tea leaves. It is not only highly efficient but also preserves the original flavor of the coffee or tea. Most importantly, the solvent can be recycled and reused, saving production costs.
It is primarily used as an organic solvent, participating in various processes such as synthesis, separation, purification, and analysis. Due to its unique properties, it is an indispensable solvent in laboratories, but due to its toxicity, it must be used with caution and according to established safety protocols.
Methylene Chloride is a Class 2 carcinogen and can easily cause liver and lung cancer. Short-term exposure to high concentrations of Methylene Chloride can lead to acute poisoning, while long-term exposure to low concentrations can result in chronic poisoning. For factories that use large quantities of Methylene Chloride, it is essential to prioritize the use of enclosed equipment and provide employees with professional protective equipment.
Benefits of Methylene Chloride
- Excellent solubility: It can dissolve a variety of organic compounds (such as resins, oils, APIs, etc.)
- Non-flammable: Methylene Chlorideis non-flammable at normal temperature and pressure.
- High volatility: This not only accelerates the reaction rate but also allows for operation in a closed system, reducing losses and improving efficiency.
- Easy to separate and extract: It is immiscible with water and has a density greater than water, which facilitates the formation of distinct layers during liquid separation, making extraction easier.
Dangers of Methylene Chloride
- It has a pungent odor; ensure proper ventilation or use it in a sealed environment to avoid harm to the human body.
- Methylene Chloridecan damage the ozone layer; handle it with caution during use to avoid environmental pollution.