Brief Introduction of Iron Sucrose
CAS NO.: 8047-67-4
Appearance:brown or dark brown powder
Iron Sucrose Molecular Formula:[Na2Fe5O8(OH)•3(H2O)]n•m(C12H22O11)
Iron Sucrose Molecular Weight: 34000-60000 Da
Pack: 25kg/drum
Standard: USP, CP
What is Iron Sucrose?
Iron sucrose is a common intravenous iron supplement used to treat iron-deficiency anemia. Common brands on the market include Venofer. Iron sucrose is primarily used to treat iron-deficiency anemia. It is generally manufactured as an intravenous iron supplement. It is safer than dextran iron, with a lower probability of allergic reactions, and is currently the preferred choice for injectable iron supplements, as well as the one with the highest market share.
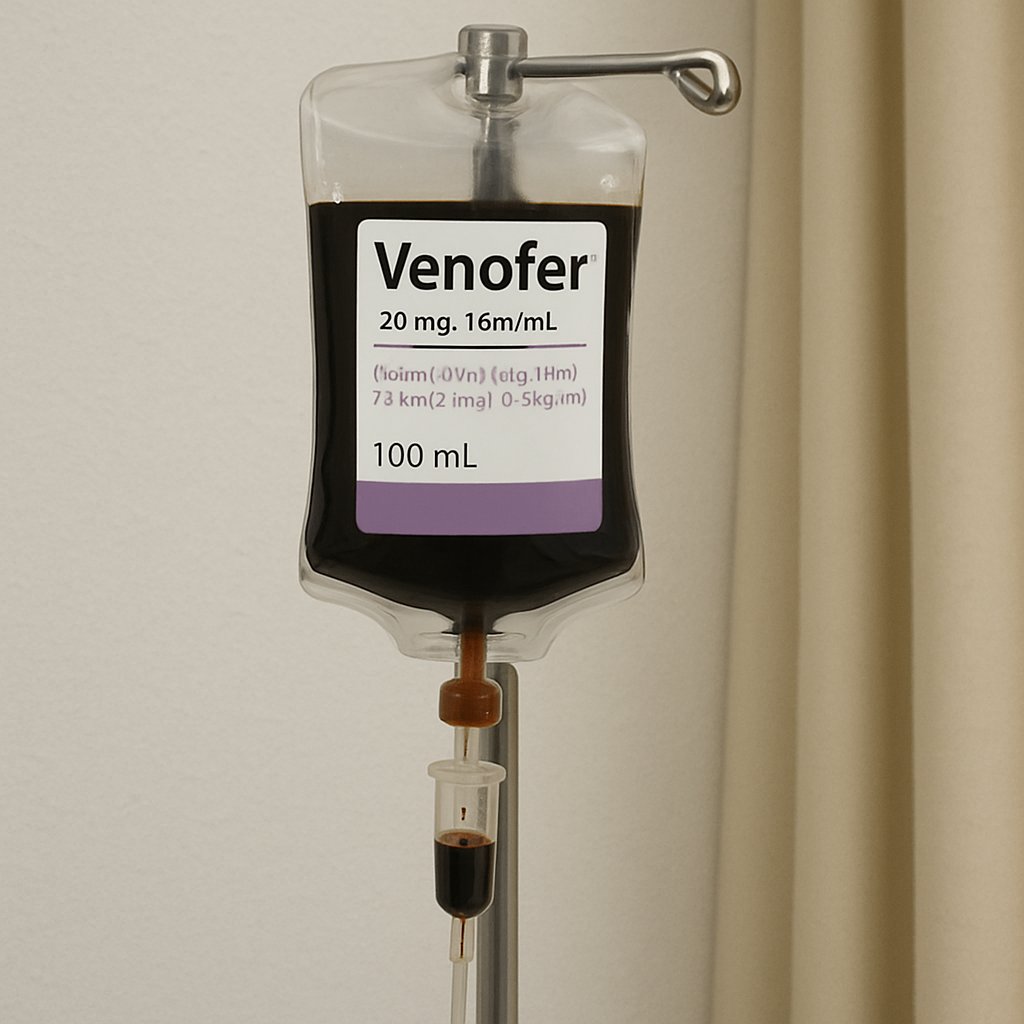
Iron Sucrose VS Iron Dextran VS Ferric Carboxymaltose
These three are all injectable iron supplements.
Iron Sucrose can only be administered as a single, small infusion. An allergy test is required. Iron Sucrose is covered by health insurance and is a regular iron supplement.
Dextran Iron can be administered as a single, large dose or a single, small infusion. An allergy test is required.
Ferric Carboxymaltose can be administered as a single, large dose. An allergy test is not required.
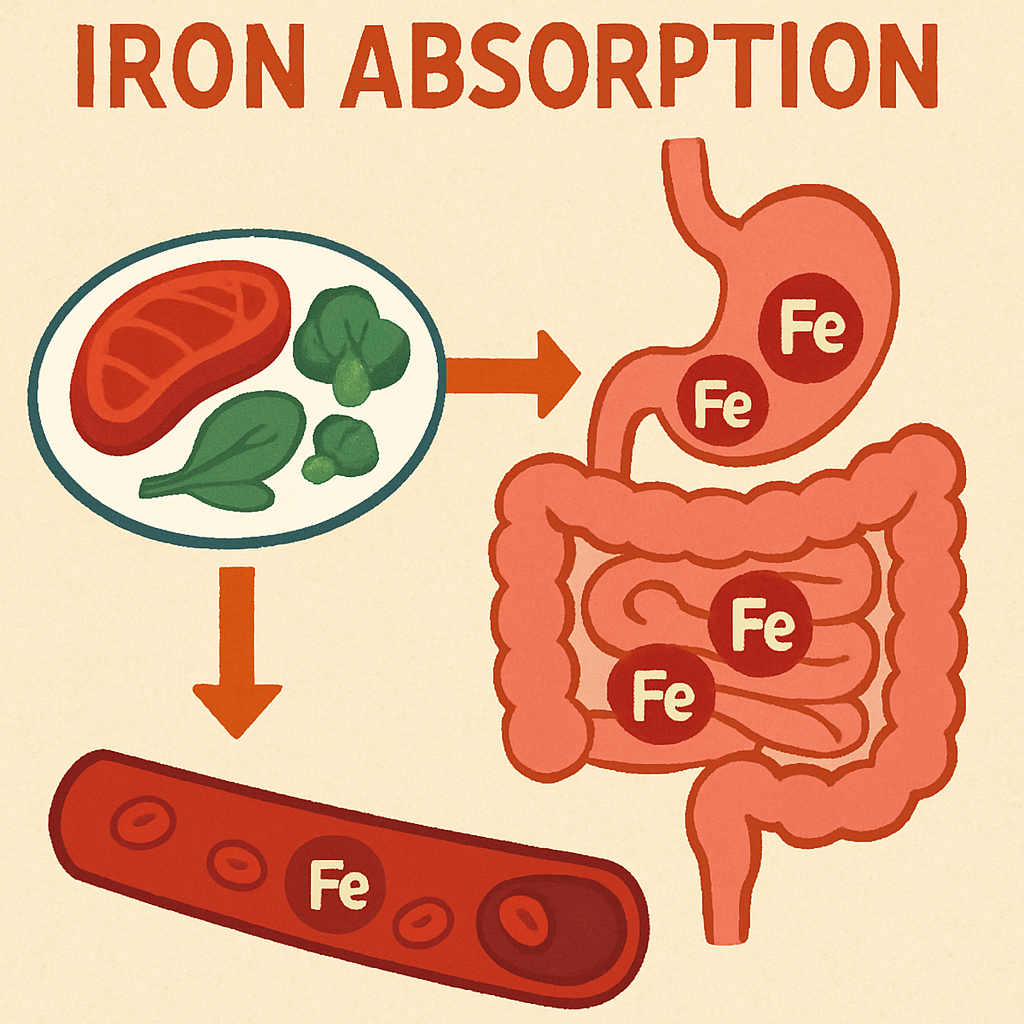
Some Ways To Improve Iron Absorption
Regardless of the type of iron supplement you choose, it’s recommended to consume it with foods or drinks high in Vitamin C, such as orange juice or grapefruit.
Avoid taking it with calcium, caffeine, or dairy products, as calcium can interfere with iron absorption.
Ferric gluconate is an oral iron supplement.
Iron sucrose is an intravenous iron supplement. The methods of administration differ.
Iron sucrose is administered intravenously and is not for oral administration.
Iron sucrose is administered intravenously and is not for oral administration.
Both are intravenous iron supplements and require an allergy test.
Dextran iron can be administered in a single large dose or multiple low doses. Sucrose iron can only be administered in multiple low doses.
Daily iron intake varies from person to person for people with anemia, but a common recommended dose is: Adults: 65 mg of iron daily (or a higher dose as prescribed by a healthcare professional).
The effectiveness of iron infusions in treating anemia symptoms varies from person to person. Typically, patients experience improved energy levels within a few days to a week, and their iron levels stabilize within a few weeks.
It varies from person to person. Some experience constipation for a few days, while others may experience it for a week or longer. Increasing intake of fiber-rich foods such as vegetables can help improve bowel movements. Increased water intake is also necessary.
Some people experience constipation after receiving iron infusions, possibly for two reasons:
- Some of the iron absorbed by the body is absorbed by the intestines, altering bowel habits.
- The body doesn’t replenish the increased iron levels with adequate hydration.
From a scientific perspective, there is no direct evidence that iron infusions cause weight gain. The treatment itself does not cause weight gain.
However, some patients have reported weight gain. The actual reasons are as follows: Fluid retention: The infusion causes a temporary accumulation of more fluid in the body, but this is temporary.
Improved appetite leading to increased food intake: Improved health and increased metabolism after iron infusions make you feel hungrier, potentially leading to more frequent or larger meals, which directly contributes to weight gain.
Fatigue: Rest more and ensure your body has enough time to recover.
Diarrhea: Maintain a balanced diet. If diarrhea is severe, you can take some antidiarrheal medication.
Dark urine: Drink more water. Observe and monitor the condition; generally, no additional intervention is needed.
Fatigue: This is likely because the body needs to work harder to process the newly infused iron, increasing its workload and causing fatigue. However, this fatigue is temporary and will improve as the body adapts.
Gastrointestinal Discomfort: Some patients experience diarrhea after infusion. Iron infusions can indeed cause digestive upset, although this is not common. If diarrhea occurs, it is usually temporary.
Darkened Urine: Darkened urine is due to increased iron metabolism and is usually a short-term effect.
Related Products
Advantages and Disadvantages of Iron Sucrose
Advantages
Low risk of allergies; the probability of an allergic reaction is very small.
Good tolerability; most patients tolerate iron sucrose well with virtually no side effects.
Disadvantages
Requires multiple infusions to achieve the desired iron level; a single large-dose infusion is not possible. This may not be very convenient. The cost of administering the same dose of iron is higher than with dextran
Iron sucrose is administered intravenously and is not for oral administration.
Under normal circumstances, a single dose of 100-200 mg is recommended, and multiple low-dose administrations are possible. A 100 mg infusion time of 15 minutes can be used as a reference, with other doses administered proportionally over this period.
Common symptoms include low blood pressure, nausea, and lower back pain.
It contains low molecular weight dextran iron and carboxylated maltose iron.
Ferrous Sulfate, Ferrous Gluconate, Ferrous Fumarate
The time depends on the individual’s health condition and the severity of the iron deficiency; it usually improves after a few days.
Insufficient intake of iron-rich foods, excessive menstrual bleeding, gastrointestinal bleeding, excessive blood loss due to injury, poor absorption due to limited gastrointestinal function, pregnancy, or rapid growth spurts.
Feeling fatigued because the body isn’t getting enough oxygen;
feeling cold, even in warm environments, with cold hands and feet; dizziness and lightheadedness due to brain hypoxia;
palpitations, as the heart needs to pump blood harder, increasing its workload and potentially leading to palpitations in the long term;
Fatigue, diarrhea or gastrointestinal discomfort, and joint pain are common side effects. These side effects are usually temporary and will subside as the body adjusts. If you experience persistent side effects that do not improve, it is recommended to consult a doctor.
Iron supplements can cause darkening of the stool color, a harmless but noticeable side effect. This is a typical reaction to the presence of iron and is nothing to worry about unless accompanied by other symptoms.
Some people may experience a metallic taste in their mouth after taking iron supplements. While unpleasant, this is usually harmless. This side effect typically lessens as the body adapts.
After receiving intravenous iron infusions, urine may darken, especially after treatment with iron sucrose (Venofer). This color change is usually harmless and will subside on its own.
Increased urine output is not a common side effect of iron infusion. However, some patients experience increased urination due to multiple factors, such as increased intravenous fluid intake before or after the procedure, and anxiety or stress can also lead to frequent urination.





