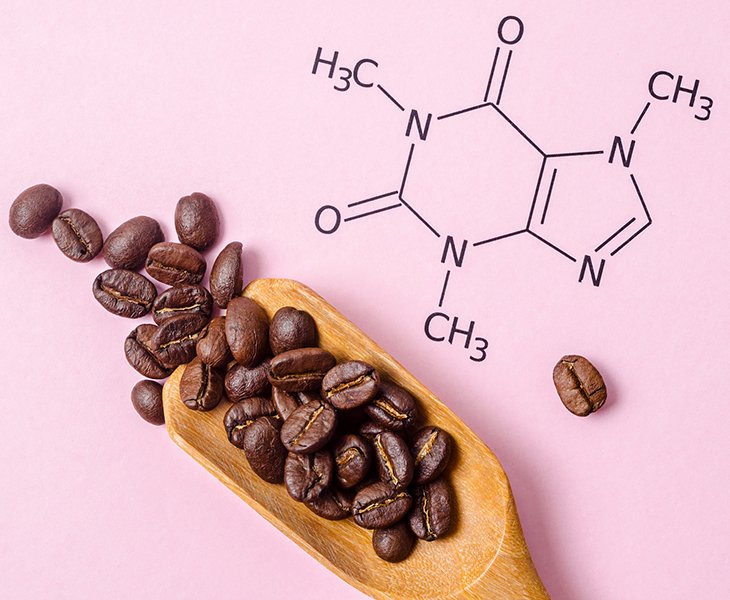
What is Anhydrous Caffeine?
- Anhydrous caffeine is pure caffeine powder that has had its water of crystallization removed. Its chemical formula is C8H10N4O2, and its CAS number is 58-08-2. Purity is usually as high as 98.5%-100%. Unlike the caffeine in regular coffee or tea, anhydrous caffeine is purified to remove water and other compounds from its natural source, making it faster-acting and more concentrated.
- Anhydrous caffeine is a xanthine alkaloid compound and is by far the most in-demand and produced variety of caffeine.
Your Leading Caffeine Anhydrous Supplier
HIGHASSAY has been offering 2 different grades of Caffeine anhydrous: pharmaceutical grade(USP/EP/BP) and food grade(FCC)
As a leading caffeine anhydrous supplier from China, we provide high-purity, premium-grade caffeine powder for food, pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, and functional products. Our products meet USP/EP/BP/FCC international standards, catering to your diverse needs!

Product by Application
Food and Beverages: As a common stimulant ingredient, it can temporarily drive away sleepiness and restore energy or increase alertness. It is often used as an additive in a variety of beverages.
 Drugs
DrugsIt can be used as a central nervous system stimulant for clinical coma resuscitation, and may have a certain auxiliary anti-inflammatory effect.
In addition, it is also suitable for combined treatment with sodium benzoate for respiratory depression caused by excessive use of central nervous system depressants.
 Cosmetics and Personal Care
Cosmetics and Personal CareCaffeine is an effective antioxidant that can neutralize free radicals and reduce oxidative damage caused by ultraviolet (UV) rays, thereby delaying skin aging.
Caffeine can reduce the dilation of eye capillaries, thereby relieving edema and fading dark circles. Many eye creams are added with caffeine to help improve “panda eyes” and morning edema.
 Dietary Supplements and Functional Foods
Dietary Supplements and Functional FoodsA moderate amount of caffeine can improve endurance sports performance.
Weight loss aid: Caffeine can slightly increase the metabolic rate and can be used as a fat-burning supplement. They are often found in nutritional supplements and weight loss pills.
Key Advantages of Highassay Caffeine Anhydrous

Dehydrated to <0.5% moisture, delivering stronger potency.

Takes effect in 15-45 minutes, more efficient than natural caffeine.

Ideal for food & beverages, pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, and weight loss supplements.

The powder form allows for precise and consistent measurement, unlike variable natural sources that may lack standardization.
Caffeine Anhydrous VS Caffeine
- Different water content.
Anhydrous caffeine does not contain crystalline water. Caffeine contains one crystalline water.
- Different molecular formulas.
The molecular formula of caffeine is C8H10N4O2, and the molecular formula of anhydrous caffeine C8H10N4O2.H2O (C8H12N4O3).
- Different molecular weights.
The molecular weight of caffeine: 194.19, and the molecular weight of anhydrous caffeine: 212.2059.

Why Partner With Highassay?

Highassay has overseas warehouses in the United States and other places, with inventory all year round, local delivery, and seamless connection.

Fully automated production line, computerized precise material feeding, temperature, and humidity control. Stable product quality, small batch quality fluctuation.

Complying with GMP production specifications, product indicators can meet multiple specifications of USP/EP/BP/FCC at the same time.

Multiple packaging options + free samples available.
More About Highassay Caffeine Anhydrous
- Summary Table
- Data Sheet
- Anhydrous caffeine VS. Natural caffeine
| Product Name | Caffeine Anhydrous |
| CAS NO. | 58-08-2 |
| Synonyms | 1,3,7-Trimethylxanthine |
| Molecular Formula | C8H10N4O2 |
| Molecular weight | 194.19 |
| Package | 20kg/carton, 25kg/drum |
| Shelf life | 5 years |
| Specification | BP/USP/FCC/EP |
| Appearance | White crystalline powder, silky, white crystals |
| Identification A | IR |
| Identification B | The retention time of the caffeine peak. |
| Appearance of solution | Clear, colorless |
| Sulfates | ≤500ppm |
| Related substances | |
| *Each impurity A/B/C/D/E/F | ≤0.10% |
| *Unspecified impurities | ≤0.10% |
| *Total impurities | ≤0.10% |
| Acidity | Not more than 0.2 mL of 0.01M sodium hydroxide |
| Organic impurities | |
| *Individual impurities | ≤0.10% |
| *Total impurities | ≤0.10% |
| Other alkaloids | No precipitate is formed |
| Melting range | 235-237.5℃ |
| Readily carbonizable substances | Passes test |
| *Loss on drying | ≤0.5% |
| Residue on ignition | ≤0.1% |
| Assay | 98.5%~101.0% |
| Mesh | ≥95% through 40 mesh |
| Odor | Odorless |
| Flavor | Bitter |
| *Heavy metal | ≤10ppm |
| *Arsenic(ICP-MS) | ≤l.5ppm |
| *Cadmium(ICP-MS) | ≤0.5ppm |
| *Lead(ICP-MS) | ≤0.5ppm |
| *Mercury(ICP-MS) | ≤0.2ppm |
| pH | 5.5-6.5 |
| Residual solvents | Chloroform ≤60ppm |
| Microbiological | |
| *Total count of Aerobic Bacteria | ≤1000cfu/g |
| *Yeast and Molds | ≤100cfu/g |
| *Escherichia coli | Negative |
| Coliforms | <10cfu/g |
| *Salmonella | Negative |
| *Staphylococcus Aureus | Negative |
| Anhydrous caffeine | Natural caffeine | |
| Form | Pure powder or capsules | Present in beverages or food
|
| Absorption rate | Fast (15-45 minutes to take effect) | Slower (affected by food ingredients)
|
| Dosage | Control Accurate (each dose is clear) | Not easy to calculate accurately |
| Other ingredients | None | Contains antioxidants, tannins, etc. |
It is safe for adults to consume no more than 400mg of anhydrous caffeine per day.
However, excessive intake (>400mg/day, about 4 cups of coffee) may bring some potential side effects, including Palpitations, anxiety, and insomnia. Gastrointestinal discomfort
Dependence (sudden discontinuation may cause headaches and fatigue)
Natural Caffeine VS. Anhydrous Caffeine VS. Caffeine Malate VS. Caffeine Citrate
Natural Caffeine
Sixty percent of adults drink caffeine every day, and most of it comes from natural sources like coffee beans, tea leaves, cocoa beans, and guarana berries.
Anhydrous Caffeine
The primary difference between natural caffeine and anhydrous caffeine lies in their water content. Anhydrous means “all the water is taken out.” Companies extract natural caffeine sources and convert them into anhydrous caffeine powder, which must contain less than 0.5% water by weight.
Anhydrous Caffeine is pure caffeine powder that has had its water of crystallization removed. Its chemical formula is C8H10N4O2, and it is typically 98%-100% pure. Unlike the caffeine in regular coffee or tea, anhydrous caffeine is its chemical formula C8H10N4O2, and it is typically 98%-100% pure. The caffeine in regular coffee or tea is different from anhydrous caffeine. Anhydrous caffeine has all the water and other stuff from its natural source taken out, so it works faster and is more powerful.
This processing and dehydration create the white, bitter crystalline powder that we all know. Anhydrous caffeine supplements on their own can quickly boost caffeine levels in the blood within 15 to 45 minutes after you take them, with the highest levels hitting between 60 to 120 minutes later.
Caffeine Malate
Also known as Infinergy™, it’s a mix of caffeine and malic acid in an ionic form, and it’s trademarked by Creative Compounds LLC.
After cocaine was banned in consumer products, Coca-Cola used caffeine malate as a replacement stimulant.
Caffeine Citrate
This compound, also called CAFCIT®, is made up of anhydrous caffeine, monohydrate citric acid, and dihydrate sodium citrate. This mix of compounds doesn’t occur in nature and needs to be made in a lab.
Even though caffeine citrate works faster than anhydrous caffeine, it has one big downside: the same amount of caffeine citrate gives you 50% less caffeine compared to the anhydrous form.





